Heat Capacity and Latent Heat
Heat Capacity and Latent Heat: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Specific Heat Capacity, Molar Heat Capacity & Molar Heat Capacity for Different Atomicities etc.
Important Questions on Heat Capacity and Latent Heat
The ratio of pressure and volume is constant and is equal to for a monoatomic gas, then the molar heat capacity at constant pressure would be-
What is R in the following equation?
Among the following statements, select the correct statements.
I. Combustion of organic compounds is an exothermic reaction.
II. There is decrease in entropy by crystallisation of a liquid into a solid.
III. The molar enthalpy of vapourisation of acetone is less than that of water.
At STP, an unknown gas of volume , requires of heat to raise its temperature by at a constant volume. The gas is
A monatomic ideal gas undergoes a process in which . What is the molar heat capacity of the gas?
of ice at is added to 340g of water at . The final temperature of the resultant mixture is . The value of (in g) is closest to
[Heat of fusion of ice ; Specific heat of water ]
Assertion: Specific heat of gas at constant pressure is greater than its specific heat at constant volume.
Reason: At constant pressure, some heat is spent in expansion of the gas.
The value of and for a gas are R and R. The vapour density of gas is . Its atomic mass will be
Equal volumes of monoatomic and diatomic gases are taken at same temperature and pressure. The ratio of adiabatic exponents of the gases will be-
A monoatomic ideal gas goes through a process in which, the ratio of to at any instance is constant and equal to unity. The molar heat capacity of gas is
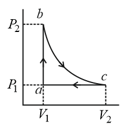
Carbon monoxide is carried around a closed cyclic process , in which is an isothermal process, as shown in the diagram. The gas absorbs of heat as its temperature is increased from to in going from to . The quantity of heat ejected by the gas during the process is
For polytropic process constant, the (molar heat capacity) of an ideal gas is given by -
For an ideal gas . The molecular mass of the gas is , its specific heat capacity at constant volume is -
moles of a tetra-atomic non-linear gas and are mixed with moles of another gas at and in a closed, rigid vessel without energy transfer with surroundings. If final temperature of mixture was , then gas is? (Assuming all modes of energy are active)
The ratio of the speed of sound in nitrogen gas to that in helium gas, at is
A monatomic ideal gas undergoes a process in which the ratio of to at any instant is constant and equal to 1. What is the molar heat capacity of the gas?
For polytropic process PVn = constant, Cm (molar heat capacity) of an ideal gas is given by :
1 mole of a gas with = 7/5 is mixed with 1 mole of a gas = 5/3, then the value of for the resulting mixture is
